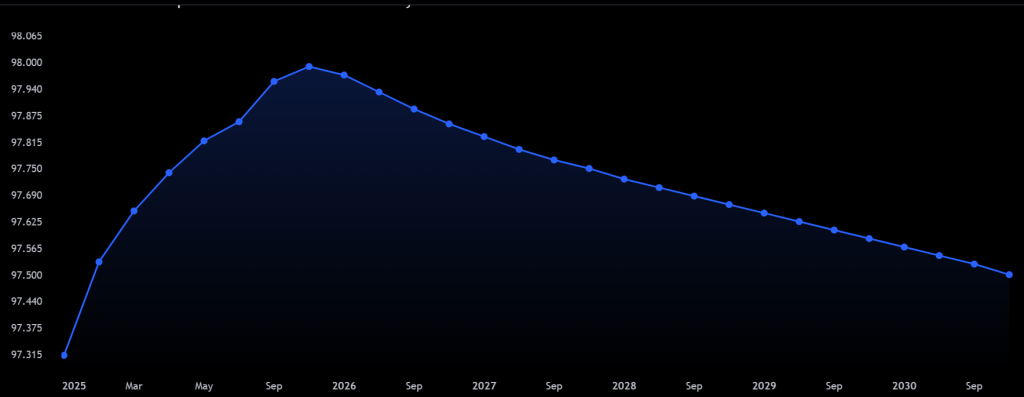
The rate is forecast to decline steadily throughout 2025. The EURIBOR (Euro Interbank Offered Rate) 3-month rate is a key interest rate in the Eurozone. It influences the cost of loans, mortgages, and other financial products. Currently, the EURIBOR 3M rate is 2.736%, but it is expected to gradually decrease over the next few years. Here’s a simple breakdown of what to expect.
- January 2025:
- Starts at 2.678% and could move between 2.436% and 2.963%.
- By the end of the month, it is expected to fall to 2.597% (a drop of -0.081 percentage points).
- February 2025:
- Begins at 2.597% and is forecast to range from 2.317% to 2.757%.
- Expected to drop to 2.465% by the end of February (-0.132 points).
- March 2025:
- Starts at 2.465%, with a maximum of 2.465% and a minimum of 2.178%.
- Ends at 2.317%, down by -0.148 points.
- April to June 2025:
- April starts at 2.317% and drops to 2.220%.
- May begins at 2.220%, ending at 2.087%.
- June opens at 2.087%, closing at 1.962%.
- July to December 2025:
- Rates will continue to decrease, ending the year at 1.740%.
Long-Term EURIBOR 3M Forecast (2026-2027)
Looking at the longer term, the EURIBOR 3M rate is expected to keep falling in 2026 and 2027.
- 2026:
- January starts at 1.740%, and by December, it could drop to 1.368%.
- 2027:
- The decline continues, with the rate forecast to be 1.358% by January.
What Does This Mean?
- Lower Borrowing Costs: As the EURIBOR 3M rate drops, loans and mortgages might become cheaper for consumers and businesses.
- Impact of ECB Policies: The forecast reflects expectations that the European Central Bank (ECB) may adopt policies to support the economy by keeping interest rates low.
- Good for Borrowers: Falling rates are generally good for borrowers but may lower returns for savers.
Keeping an eye on these rates and understanding how they affect you can help you plan for the future. The EURIBOR 3M rate is expected to steadily decline from its current level of 2.736% to 1.358% by early 2027. This trend is significant for anyone involved in borrowing, lending, or investing, as it will influence financial decisions across the Eurozone.